QuickBooks Internals | Security | Bugs
From Part 2 we know how sensitive data keys are stored and it is easy to see that QuickBooks Forensics can access protected records instantly and without user password, so there is obviously something wrong with protection methods and procedures used. These problems are outside the scope of our notes, but we will show 3 easy to test bugs that let us doubt whether QB was ever independently tested.
First step is to create new company file and add one or two additional users. No passwords, no special settings.
It's worth mentioning that "abmc_master_key", "abmc_admin_master_key" and "abmc_key_permissions" tables all have "db_created_tms" and "db_modified_tms" fields - precise SQL Anywhere timestamps. There is no need to compare stored values if timestamp is not updated.
It is easy to note that sensitive data "encryption" is "on" permanently - just open the file with QuickBooks Forensics and you will see all the tables and keys. Switching "CC Numbers Protection" will activate 90 days password change reminder and complexity check but the keys are already present.
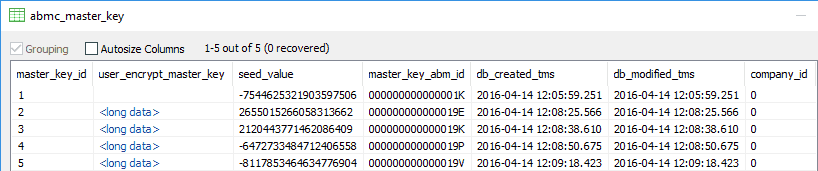
Bug 1: Open company file with QuickBooks Forensics and note "seed_value" from "abmc_master_key". Close and open with QB as Admin, change Admin password. Close and open with QuickBooks Forensics. "seed_value" is permanent!
Bug 2: Open company file with QuickBooks Forensics and copy all timestamps from "abmc_master_key". Close and open with QB, activate "CC Numbers Protection", enter new Admin password, etc. Close and open with QuickBooks Forensics. With "CC Numbers Protection" activated all other users Master keys are still the same and can be decrypted with old week (or empty) passwords. Yes QB is going to force user to change password upon new login, but inactive users can stay like this indefinitely creating extra set of keys without real protection.
Bug 3: Open company file with QuickBooks Forensics and note all timestamps from "abmc_key_permissions". Close and open with QB, remove one of the users. Close and open with QuickBooks Forensics. User additional or removal do not trigger new data keys generation and old copies of user keys can be used to access new data.
You can easily find pdf document from Intuit ("PCI_PADSS_QB2010_Implementation_Guide.pdf") with explanation how this system was designed to work and just in 10-15 minutes we showed you how to find several discrepancies.
All trademarks are the property of their respective holders.
